
Chapter 3
Sleep
“Sleep is the golden chain that ties health and our bodies together.”
– Thomas Dekker


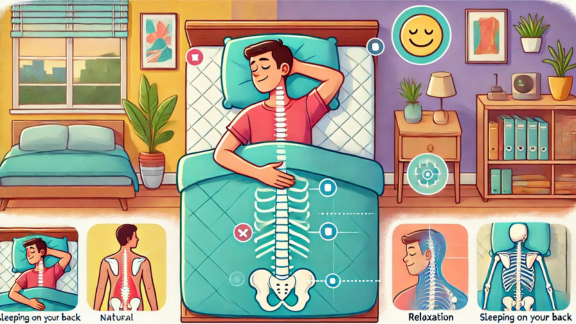
Optimal Sleep Positions
The best sleep positions are on your back or side.
These positions support natural spinal alignment and reduce pressure on your body.
Avoid sleeping on your stomach, which strains your back and applies too much pressure.






Establish a Sleep Routine
Create a pre-sleep routine to help signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
Dedicate an hour before bed to screen-free activities.
Engage in relaxing activities like reading, journaling, sudoku, light studying, or simply reflecting on your day.






Establish a Morning Routine
A set routine helps override the emotional part of your brain and sets a positive tone for the day.
For example, drink a glass of water right after waking up to hydrate.






Use the 5-Second Rule
When your alarm goes off, count 5-4-3-2-1 (out loud or in your mind) and get out of bed immediately.
This technique prevents your mind from convincing you to stay in bed.






Wake Up When Your Body is Ready
If you wake up before your alarm, get out of bed.
You likely woke at the end of a REM cycle, feeling rested.
Returning to sleep for 10-15 minutes might interrupt a REM cycle, making you feel groggy all day.






Feel free to share with your colleagues
Give feedback, ask questions or request new resources


